apollo介绍之Transform模块(七)
Transform模块介绍
关于transform模块开始一直不知道是干啥的,一直看到一个"/tf"的TOPIC,还以为是tensorflow的缩写,想着是不是和神经网络有关系,后来才知道tf是transform的缩写,主要的用途是进行坐标转换,原型即是大名鼎鼎的"ros/tf2"库。那么为什么要进行坐标转换呢?
在机器人系统中,经常需要用到坐标转换,比如一个机器人的手臂要去拿一个运动的物体,控制的时候我们需要手臂的当前坐标,同时还需要知道手臂和身体的坐标,这个时候就需要用到坐标转换,把手臂的坐标转换为身体的坐标系,这样控制起来就方便一点。当然这里是动态的情况,也存在静态的情况,比如机器人头顶的摄像头,转换到身体的坐标系,那么位置关系是相对固定的,所以可以一开始就写到固定的位置。这里就引入了以下几个问题:
- 有固定转换关系的文件放在哪里?如果都是集中放在一个地方,那么这个地方损坏会导致所有的转换关系失效,一个比较好的方法是各个节点自己广播自己的转换关系。而其实静态的转换关系只需要发送一次就可以了,因为不会变化。
- 有动态转换关系的节点,需要实时动态发布自己的转换关系,这样会涉及到时间戳,以及过时。
- 转换关系的拓扑结构如何确定?是树型还是网络型的,这涉及到转换关系传递的问题。
Transform(静态变换)
TransformComponent模块的入口在""和"static_transform_component.h"中。实现了"StaticTransformComponent"类,我们接下来看下它的实现。
class StaticTransformComponent final : public apollo::cyber::Component<> {public:StaticTransformComponent() = default; // 构造函数~StaticTransformComponent() = default; // 析构函数public:bool Init() override; // 初始化函数private:void SendTransforms(); // 发送变换void SendTransform(const std::vector<TransformStamped>& msgtf); //发送变换,参数为数组bool ParseFromYaml(const std::string& file_path, TransformStamped* transform); // 从yaml中解析apollo::static_transform::Conf conf_; // 配置文件std::shared_ptr<cyber::Writer<TransformStampeds>> writer_; // cyber node写句柄TransformStampeds transform_stampeds_; // 变换关系,在proto中定义};
下面我们来分析StaticTransformComponent类具体的实现,首先是Init函数,Init函数做了2件事情,一是读取conf配置,二是发布"/tf_static"消息。
bool StaticTransformComponent::Init() {// 读取配置if (!GetProtoConfig(&conf_)) {AERROR << "Parse conf file failed, " << ConfigFilePath();return false;}// 发布消息cyber::proto::RoleAttributes attr;attr.set_channel_name("/tf_static");attr.mutable_qos_profile()->CopyFrom(cyber::transport::QosProfileConf::QOS_PROFILE_TF_STATIC);// 注意这里的node_继承至apollo::cyber::Componentwriter_ = node_->CreateWriter<TransformStampeds>(attr);SendTransforms();return true;}
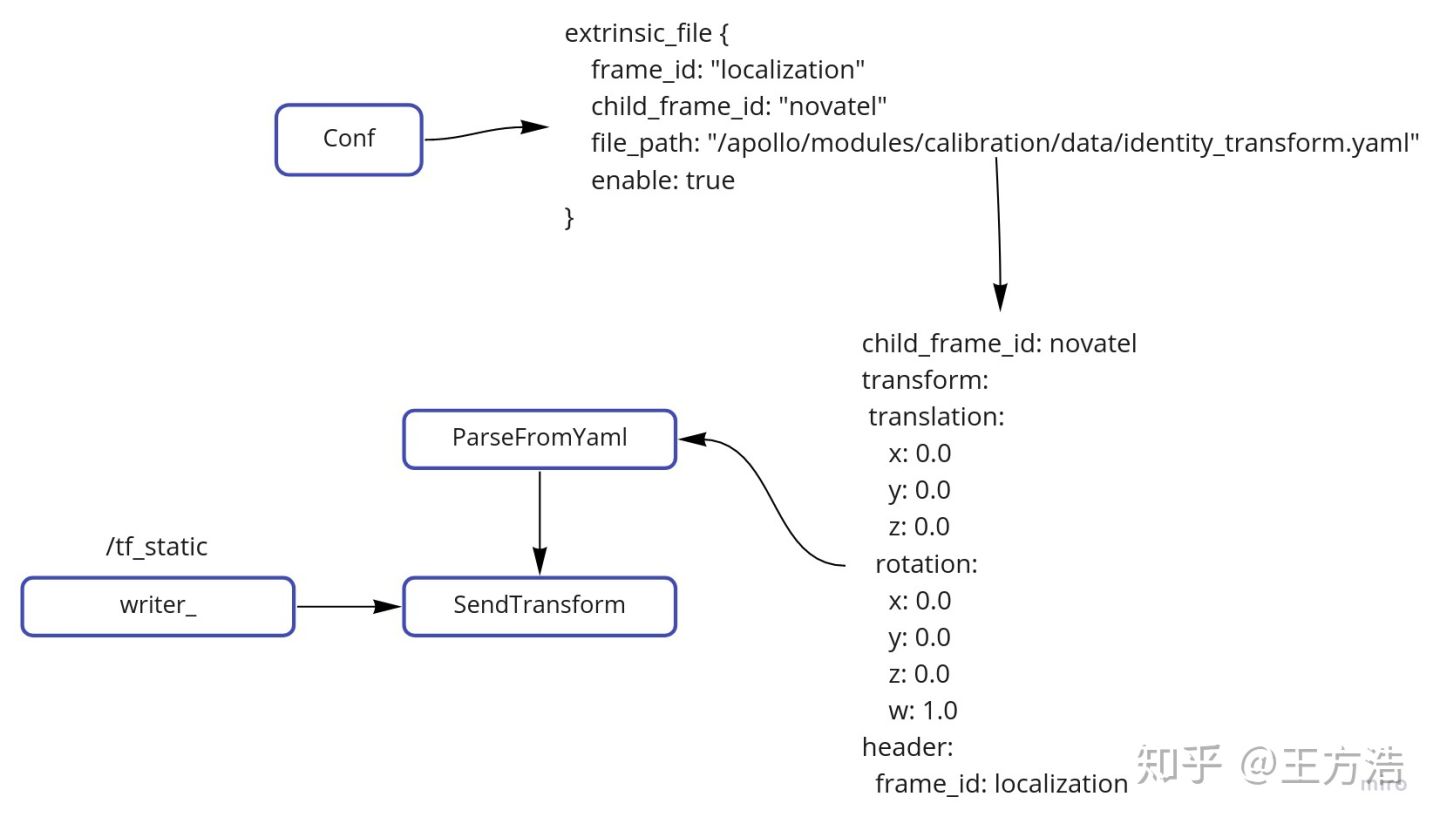
接着看SendTransforms()函数,主要就是遍历conf文件,判断extrinsic_file(实际上对应各种传感器的外参)是否使能,如果使能则根据提供的文件路径解析对应的转换关系"ParseFromYaml",把转换关系添加到数组"tranform_stamped_vec"中,然后发送。
void StaticTransformComponent::SendTransforms() {std::vector<TransformStamped> tranform_stamped_vec;// 遍历对应的文件,实际上对应各种传感器的外参for (auto& extrinsic_file : conf_.extrinsic_file()) {// 是否使能if (extrinsic_file.enable()) {AINFO << "Broadcast static transform, frame id ["<< extrinsic_file.frame_id() << "], child frame id ["<< extrinsic_file.child_frame_id() << "]";TransformStamped transform;// 解析yaml文件,获取转换,并且添加到数组中if (ParseFromYaml(extrinsic_file.file_path(), &transform)) {tranform_stamped_vec.emplace_back(transform);}}}// 发送对应的转换SendTransform(tranform_stamped_vec);}
解析yaml需要注意的地方,在conf中的frame_id和child_id实际上没有使用,最后还是以yaml文件中的为准。其中yaml文件的格式为:
child_frame_id: novateltransform:translation:x: 0.0y: 0.0z: 0.0rotation:x: 0.0y: 0.0z: 0.0w: 1.0header:frame_id: localization
我们在看下如何解析yaml文件:
bool StaticTransformComponent::ParseFromYaml(const std::string& file_path, TransformStamped* transform_stamped) {...YAML::Node tf = YAML::LoadFile(file_path);try {// 读取yaml文件中的frame_id和child_frame_idtransform_stamped->mutable_header()->set_frame_id(tf["header"]["frame_id"].as<std::string>());transform_stamped->set_child_frame_id(tf["child_frame_id"].as<std::string>());// translation 位置auto translation =transform_stamped->mutable_transform()->mutable_translation();translation->set_x(tf["transform"]["translation"]["x"].as<double>());translation->set_y(tf["transform"]["translation"]["y"].as<double>());translation->set_z(tf["transform"]["translation"]["z"].as<double>());// rotation 角度auto rotation = transform_stamped->mutable_transform()->mutable_rotation();rotation->set_qx(tf["transform"]["rotation"]["x"].as<double>());rotation->set_qy(tf["transform"]["rotation"]["y"].as<double>());rotation->set_qz(tf["transform"]["rotation"]["z"].as<double>());rotation->set_qw(tf["transform"]["rotation"]["w"].as<double>());} catch (...) {AERROR << "Extrinsic yaml file parse failed: " << file_path;return false;}return true;}
最后我们再看下如何发送转换关系:
void StaticTransformComponent::SendTransform(const std::vector<TransformStamped>& msgtf) {for (auto it_in = msgtf.begin(); it_in != msgtf.end(); ++it_in) {bool match_found = false;int size = transform_stampeds_.transforms_size();// 如果child_frame_id重复,那么则覆盖对应的配置for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {if (it_in->child_frame_id() ==transform_stampeds_.mutable_transforms(i)->child_frame_id()) {auto it_msg = transform_stampeds_.mutable_transforms(i);*it_msg = *it_in;match_found = true;break;}}if (!match_found) {// 获取增加的指针地址,并且赋值auto ts = transform_stampeds_.add_transforms();*ts = *it_in;}}writer_->Write(std::make_shared<TransformStampeds>(transform_stampeds_));}
所以这里需要注意child_frame_id的值一定不要一样,否则会覆盖之前的配置。
按照流程总结一下就如下图所示,首先遍历conf,获取传感器的外参数文件路径,然后解析对应的yaml文件,并且发布到"/tf_static"。
transform_broadcaster(广播)
我们再来看下transform_broadcaster(广播消息),transform_broadcaster只是做为一个lib库提供给其他模块,入口在"transform_broadcaster.h"和""中。
class TransformBroadcaster {public:// 这里注意构造的时候需要传入nodeexplicit TransformBroadcaster(const std::shared_ptr<cyber::Node>& node);// 发送单个转换关系void SendTransform(const TransformStamped& transform);// 发送一组转换关系void SendTransform(const std::vector<TransformStamped>& transforms);private:std::shared_ptr<cyber::Node> node_;std::shared_ptr<cyber::Writer<TransformStampeds>> writer_;};
从上面的分析可以看出,构造TransformBroadcaster的时候需要传入node。为什么需要传入node呢,因为cyber的一个module不能同时创建8678个node,所以这里谁调用,就用谁的node创建reader和writer。如果是自己创建node,那么其他模块自己的node和引用该模块创建的node就打破了cyber上述的限制,这里的node是否可以理解为一个进程?
下面我们分析具体的实现,首先是TransformBroadcaster构造函数:
TransformBroadcaster::TransformBroadcaster(const std::shared_ptr<cyber::Node>& node): node_(node) {cyber::proto::RoleAttributes attr;// 发布的topic为"/tf"attr.set_channel_name("/tf");writer_ = node_->CreateWriter<TransformStampeds>(attr);}
创建writer并且往"/tf"发消息。这里可以看到,这里存在多个节点往一个topic发消息的情况。
发送消息比较简单,直接写对应的消息:
void TransformBroadcaster::SendTransform(const std::vector<TransformStamped>& transforms) {auto message = std::make_shared<TransformStampeds>();*message->mutable_transforms() = {transforms.begin(), transforms.end()};writer_->Write(message);}
Buffer
Buffer实际上提供了一个工具类给其他模块,它的主要作用是接收"/tf"和"/tf_static"的消息,并且保持在buffer中,提供给其他的节点进行查找和转换到对应的坐标系,我们先看BufferInterface的实现:
BufferInterface
class BufferInterface {public:// 根据frame_id获取2帧的转换关系virtual apollo::transform::TransformStamped lookupTransform(const std::string& target_frame, const std::string& source_frame,const cyber::Time& time, const float timeout_second = 0.01f) const = 0;// 根据frame_id获取2帧的转换关系,假设固定帧???virtual apollo::transform::TransformStamped lookupTransform(const std::string& target_frame, const cyber::Time& target_time,const std::string& source_frame, const cyber::Time& source_time,const std::string& fixed_frame,const float timeout_second = 0.01f) const = 0;// 测试转换是否可行virtual bool canTransform(const std::string& target_frame,const std::string& source_frame,const cyber::Time& time,const float timeout_second = 0.01f,std::string* errstr = nullptr) const = 0;// 测试转换是否可行virtual bool canTransform(const std::string& target_frame,const cyber::Time& target_time,const std::string& source_frame,const cyber::Time& source_time,const std::string& fixed_frame,const float timeout_second = 0.01f,std::string* errstr = nullptr) const = 0;// Transform, simple api, with pre-allocation// 预分配内存template <typename T>T& transform(const T& in, T& out, const std::string& target_frame, // NOLINTfloat timeout = 0.0f) const {// do the transformtf2::doTransform(in, out, lookupTransform(target_frame, tf2::getFrameId(in),tf2::getTimestamp(in), timeout));return out;}// transform, simple api, no pre-allocation// 没有预分配内存template <typename T>T transform(const T& in, const std::string& target_frame,float timeout = 0.0f) const {T out;return transform(in, out, target_frame, timeout);}// transform, simple api, different types, pre-allocation// 不同的类型template <typename A, typename B>B& transform(const A& in, B& out, const std::string& target_frame, // NOLINTfloat timeout = 0.0f) const {A copy = transform(in, target_frame, timeout);tf2::convert(copy, out);return out;}// Transform, advanced api, with pre-allocationtemplate <typename T>T& transform(const T& in, T& out, const std::string& target_frame, // NOLINTconst cyber::Time& target_time, const std::string& fixed_frame,float timeout = 0.0f) const {// do the transformtf2::doTransform(in, out, lookupTransform(target_frame, target_time, tf2::getFrameId(in),tf2::getTimestamp(in), fixed_frame, timeout));return out;}// transform, advanced api, no pre-allocationtemplate <typename T>T transform(const T& in, const std::string& target_frame,const cyber::Time& target_time, const std::string& fixed_frame,float timeout = 0.0f) const {T out;return transform(in, out, target_frame, target_time, fixed_frame, timeout);}// Transform, advanced api, different types, with pre-allocationtemplate <typename A, typename B>B& transform(const A& in, B& out, const std::string& target_frame, // NOLINTconst cyber::Time& target_time, const std::string& fixed_frame,float timeout = 0.0f) const {// do the transformA copy = transform(in, target_frame, target_time, fixed_frame, timeout);tf2::convert(copy, out);return out;}};
BufferInterface实现的功能主要是查找转换关系,以及查看转换关系是否存在,以及做最后的转换。
Buffer
下面我们接着看buffer类的实现,可以看到buffer类继承了"BufferInterface"和"tf2::BufferCore",其中"tf2::BufferCore"就是大名鼎鼎的ROS中的tf2库。
class Buffer : public BufferInterface, public tf2::BufferCore {public:using tf2::BufferCore::canTransform;using tf2::BufferCore::lookupTransform;// 构造buffer objectint Init();// 根据frame_id获取2帧的转换关系,继承至BufferInterfacevirtual apollo::transform::TransformStamped lookupTransform(const std::string& target_frame, const std::string& source_frame,const cyber::Time& time, const float timeout_second = 0.01f) const;// 继承至BufferInterfacevirtual apollo::transform::TransformStamped lookupTransform(const std::string& target_frame, const cyber::Time& target_time,const std::string& source_frame, const cyber::Time& source_time,const std::string& fixed_frame, const float timeout_second = 0.01f) const;// 继承至BufferInterfacevirtual bool canTransform(const std::string& target_frame,const std::string& source_frame,const cyber::Time& target_time,const float timeout_second = 0.01f,std::string* errstr = nullptr) const;// 继承至BufferInterfacevirtual bool canTransform(const std::string& target_frame,const cyber::Time& target_time,const std::string& source_frame,const cyber::Time& source_time,const std::string& fixed_frame,const float timeout_second = 0.01f,std::string* errstr = nullptr) const;private:// 转换回调???void SubscriptionCallback(const std::shared_ptr<const apollo::transform::TransformStampeds>&transform);void StaticSubscriptionCallback(const std::shared_ptr<const apollo::transform::TransformStampeds>&transform);void SubscriptionCallbackImpl(const std::shared_ptr<const apollo::transform::TransformStampeds>&transform,bool is_static);void AsyncSubscriptionCallbackImpl(const std::shared_ptr<const apollo::transform::TransformStampeds>&transform,bool is_static);// 转换tf2消息为cyber protobuf格式void TF2MsgToCyber(const geometry_msgs::TransformStamped& tf2_trans_stamped,apollo::transform::TransformStamped& trans_stamped) const; // NOLINTstd::unique_ptr<cyber::Node> node_;std::shared_ptr<cyber::Reader<apollo::transform::TransformStampeds>>message_subscriber_tf_;std::shared_ptr<cyber::Reader<apollo::transform::TransformStampeds>>message_subscriber_tf_static_;cyber::Time last_update_;std::vector<geometry_msgs::TransformStamped> static_msgs_;// 单例DECLARE_SINGLETON(Buffer)}; // class
这里注意buffer为单例模式,即接收转换消息,并且放到buffer中保存。其他模块需要用到转换的时候,则从buffer中查找是否存在转换关系,并且进行对应的转换。
下面我们看buffer类的具体实现,buffer类的初始化在Init函数中:
int Buffer::Init() {std::string node_name ="transform_listener_" + std::to_string(cyber::Time::Now().ToNanosecond());// 创建node节点node_ = cyber::CreateNode(node_name);cyber::ReaderConfig tf_reader_config;// 读取"/tf"消息tf_reader_config.channel_name = "/tf";tf_reader_config.pending_queue_size = 5;message_subscriber_tf_ =node_->CreateReader<apollo::transform::TransformStampeds>(tf_reader_config,[&](const std::shared_ptr<const apollo::transform::TransformStampeds>&msg_evt) { SubscriptionCallbackImpl(msg_evt, false); });// 读取"/tf_static"消息apollo::cyber::proto::RoleAttributes attr_static;attr_static.set_channel_name("/tf_static");attr_static.mutable_qos_profile()->CopyFrom(apollo::cyber::transport::QosProfileConf::QOS_PROFILE_TF_STATIC);message_subscriber_tf_static_ =node_->CreateReader<apollo::transform::TransformStampeds>(attr_static,[&](const std::shared_ptr<apollo::transform::TransformStampeds>&msg_evt) { SubscriptionCallbackImpl(msg_evt, true); });return cyber::SUCC;}
可以看到在Init函数中主要实现的功能是创建节点,并且订阅"/tf"和"/tf_static"消息,由于Buffer为单例,在cyber初始化的时候创建的node,不是在模块内部创建的node(关于这块,后面有时间在详细论述下,cyber可以存在多个node,而启动的模块则不能,是不是因为cyber做为调度器,为了方便控制)。
回调函数都是SubscriptionCallbackImpl,我们看下它是如何缓存消息的?
void Buffer::SubscriptionCallbackImpl(const std::shared_ptr<const apollo::transform::TransformStampeds>& msg_evt,bool is_static) {cyber::Time now = cyber::Time::Now();// authority的用途???std::string authority ="cyber_tf"; // msg_evt.getPublisherName(); // lookup the authority// 看起来不可能进入这个条件,除非多线程???if (now.ToNanosecond() < last_update_.ToNanosecond()) {AINFO << "Detected jump back in time. Clearing TF buffer.";clear();// cache static transform stamped again.for (auto& msg : static_msgs_) {setTransform(msg, authority, true);}}last_update_ = now;for (int i = 0; i < msg_evt->transforms_size(); i++) {try {// 封装消息geometry_msgs::TransformStamped trans_stamped;// headerconst auto& header = msg_evt->transforms(i).header();trans_stamped.header.stamp =static_cast<uint64_t>(header.timestamp_sec() * kSecondToNanoFactor);trans_stamped.header.frame_id = header.frame_id();trans_stamped.header.seq = header.sequence_num();// child_frame_idtrans_stamped.child_frame_id = msg_evt->transforms(i).child_frame_id();// translationconst auto& transform = msg_evt->transforms(i).transform();trans_stamped.transform.translation.x = transform.translation().x();trans_stamped.transform.translation.y = transform.translation().y();trans_stamped.transform.translation.z = transform.translation().z();// rotationtrans_stamped.transform.rotation.x = transform.rotation().qx();trans_stamped.transform.rotation.y = transform.rotation().qy();trans_stamped.transform.rotation.z = transform.rotation().qz();trans_stamped.transform.rotation.w = transform.rotation().qw();// 保存静态转换,用于上面判断条件的时候,重新设置静态转换if (is_static) {static_msgs_.push_back(trans_stamped);}// 调用tf2的函数,保存转换到cache,区分静态和动态的转换setTransform(trans_stamped, authority, is_static);} catch (tf2::TransformException& ex) {std::string temp = ex.what();AERROR << "Failure to set recieved transform:" << temp.c_str();}}}
接着是lookupTransform和canTransform分别调用tf2的库函数,实现查找转换和判断是否能够转换的实现,由于函数功能比较简单这里就不介绍了。
可以看到主要的缓存实现都是在tf2的库函数中,后面有时间再分析下tf2具体的实现。
todo
tf_static的问题:
1. 为什么把obs_sensor2novatel_tf2_frame_id改为localization了???
2. 为什么发布的时候需要传入node,即多个node往一个topic发送,还是说多个线程访问同一个node(location和perception同时通过一个node发布topic)?
3. 为什么需要根据child_frame_id做过滤,即使child_frame_id不能一样,否则会后面会覆盖前面的?(StaticTransformComponent::SendTransform)
4. 订阅的时候是每个模块都有listener吗,即遵循tf的设计原则。即代码可以复用,但是实例是每个模块自己new一个。
5. Buffer::SubscriptionCallbackImpl 中为什么时间戳比更新就清空整个List?
if (now.ToNanosecond() < last_update_.ToNanosecond()) {AINFO << "Detected jump back in time. Clearing TF buffer.";clear();// cache static transform stamped again.for (auto& msg : static_msgs_) {setTransform(msg, authority, true);}}
6. Buffer是一个单例,"apollo::transform::Buffer"提供了查询接口,即每个模块共享这个单例,和tf的设计原则还是不相符合? 注意线程安全?